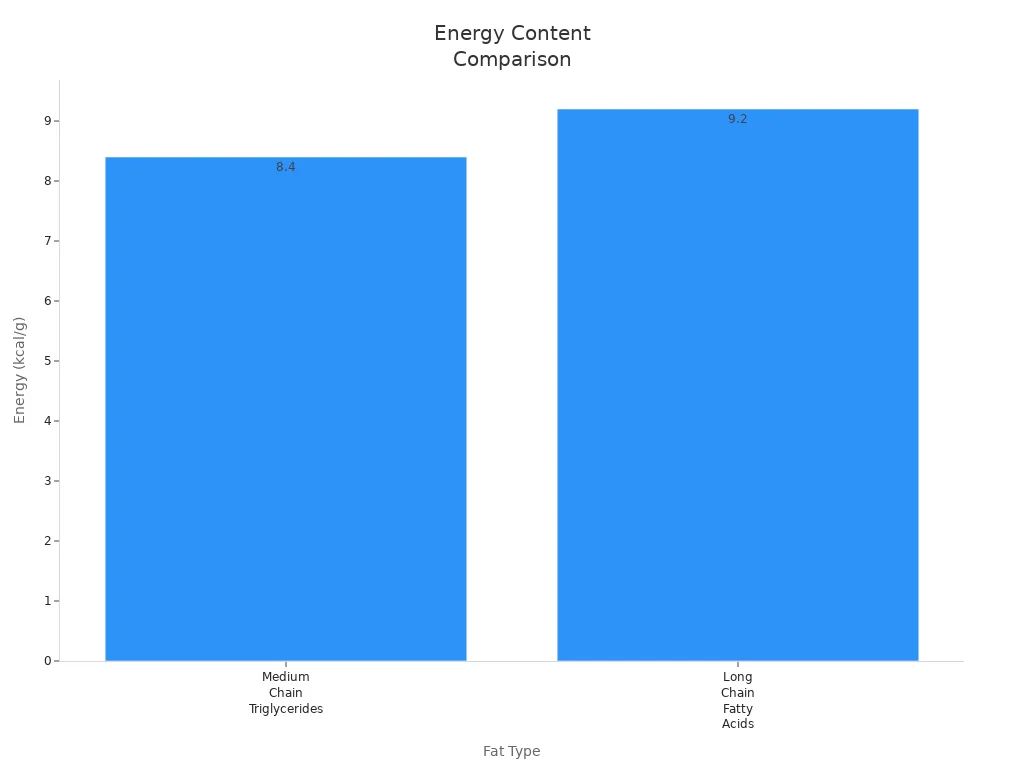
You may see that medium chain triglycerides and long-chain fatty acids work in different ways in your body. Medium chain triglycerides move fast through your stomach and go right to your liver. There, they give you energy quickly. Long-chain fatty acids take longer to break down. They are stored as fat more often. New studies show that medium chain triglycerides give a little less energy than long-chain fatty acids.
If you want to make good choices about fat, knowing these facts can help you pick what is best for your energy and health.
Key Takeaways
Medium chain triglycerides give you fast energy. They go right into your blood and then to your liver.
Long-chain fatty acids take more time to break down. Your body often keeps them as fat. They give you energy slowly.
You can get MCTs from coconut oil for quick energy. This is helpful if you have a hard time with fats.
You can get LCFAs from fish and nuts. These foods help your heart and brain stay healthy.
Eating both MCTs and LCFAs can help you control your weight. It can also help you feel more energetic.
What Are Triglycerides?

Definition
Triglycerides are a kind of fat in your blood. You get them from foods like oils, butter, and meat. Your body makes triglycerides when you eat too many calories. These fats save energy for later. When you eat more than you need, your body turns extra calories into triglycerides. It keeps them in fat cells.
Tip: You can find out your triglyceride levels with a blood test. Doctors use this test to check if you have too much fat in your blood.
Many people have high triglyceride levels. More than 25% of adults in the United States have levels of 150 mg/dl or higher. This means about 56.9 million people have high levels. If you take statins, you might still have high triglycerides. About 31.6% of people who use statins have this issue. These facts show that triglycerides matter for your health.
Role in the Body
Triglycerides do many important jobs. They store energy and help your body use fuel when needed. Your cells break down triglycerides to get fatty acids. These fatty acids go to your mitochondria. There, they help make ATP, which gives your cells energy.
Here is a table that shows how triglycerides work in your body:
Functions | Description |
|---|---|
Neurons use lipid droplets with triglycerides for energy, especially when glucose is low. | |
Triglycerides are a backup fuel for your brain when glucose is not there. | |
Neuronal Energy Production | Fatty acids from triglycerides move to mitochondria for ATP, helping brain activity. |
Triglycerides also help your brain. Neurons use them for energy when glucose is gone. The enzyme DDHD2 breaks down triglycerides in neurons. If DDHD2 does not work, you may have trouble with memory and thinking. Scientists think changes in triglyceride metabolism may link to diseases like Parkinson’s.
Triglycerides help your body in many ways.
They help your cells make energy.
They may affect your brain and thinking skills.
Medium Chain Triglycerides vs Long-Chain Fatty Acids
Structure
The main difference between medium chain triglycerides and long-chain fatty acids is their carbon chain length. Medium chain triglycerides have 6 to 12 carbon atoms. Long-chain fatty acids have 13 or more carbon atoms. This chain length changes how your body uses each fat.
Here is a table that shows the carbon chain length for different types of fatty acids:
Type of Fatty Acid | Carbon Chain Length |
|---|---|
Short-Chain Fatty Acids | 2 to 5 carbon atoms |
Medium Chain Triglycerides | 6 to 12 carbon atoms |
Long-Chain Fatty Acids | 13 or more carbon atoms |
Chain length does more than just count carbons. Short-chain fatty acids mix well with water. Medium chain triglycerides mix with water a little. Long-chain fatty acids do not mix with water much. Your body absorbs each type in a different way. Short-chain fatty acids move through cell walls easily. Medium chain triglycerides need bile salts to break up. Long-chain fatty acids join with other things to get absorbed.
Chain Type | Carbon Length | Solubility Characteristics | Absorption Mechanism |
|---|---|---|---|
Short-Chain Fatty Acids | C2-C5 | High aqueous solubility | Membrane diffusion |
Medium Chain Triglycerides | C6-C12 | Moderate solubility | Bile salt emulsification |
Long-Chain Fatty Acids | ≥C13 | Low solubility | Mixed micelle formation |
Fat emulsions help your body digest and absorb these fats. The structure of each type changes how fast you get energy and how your body stores fat.
Note: The structure of medium chain triglycerides lets your body use them fast for energy. Long-chain fatty acids break down slowly and get stored as fat.
Dietary Sources
You find medium chain triglycerides in only a few foods. Coconut oil and dairy fat have the most. Most plant oils and animal fats have mostly long-chain fatty acids. People eat more long-chain fatty acids than medium chain triglycerides in their diets.
Here are some common sources for each type:
Medium Chain Triglycerides:
Coconut oil
Dairy fat (like butter and cheese)
Long-Chain Fatty Acids:
Olive oil
Canola oil
Sunflower oil
Meat
Fish
Eggs
Short-chain fatty acids come from fiber breaking down in your gut. You do not get them straight from food.
Most people eat only a little medium chain triglycerides. For example, Japanese adults eat about 300 mg of medium-chain fatty acids each day. People get much more long-chain fatty acids because they are in many foods.
Tip: If you want more medium chain triglycerides, use coconut oil or eat more dairy fat.
Now you know that the structure and sources of these fats matter. This helps you make better choices for your health.
Digestion and Absorption
MCTs Absorption
When you eat foods with medium chain triglycerides, your body treats them differently. These fats move fast through your stomach and small intestine. Your body does not need to break them down a lot. Medium chain triglycerides go straight into your blood through the portal vein. They skip the usual steps that other fats need. Your liver gets these fats quickly and uses them for energy right away. You do not need much help from bile salts or fat emulsions to absorb them. This makes medium chain triglycerides a good choice for people who have trouble digesting fat.
LCTs Absorption
Long-chain fatty acids take a different path in your body. Your body works harder to break them down. First, your pancreas sends out special enzymes called lipases. These enzymes break the fat into smaller pieces. Next, bile from your gallbladder mixes with the fat to make fat emulsions. This step is important for your body to absorb the fat. The small fat droplets then form micelles. Your intestine can absorb these micelles. After absorption, your body puts the fats back together and wraps them in chylomicrons. These chylomicrons go into your lymph system before they reach your blood. This whole process takes longer and has more steps.
Key Differences
You can see the main differences in this table:
Aspect | Medium-Chain Triglycerides (MCTs) | Long-Chain Fatty Acids (LCTs) |
|---|---|---|
Absorption Mechanism | Absorbed directly into portal circulation | Requires micellar solubilization |
Hydrolysis Rate | Rapid hydrolysis | Slower hydrolysis |
Dependence on Pancreatic Lipase | Can be absorbed intact without it | Requires pancreatic lipase |
Effect on Gallbladder | Does not stimulate contraction | Stimulates contraction |
Presence in Lymph | Sparingly found, mostly in mixed form | Commonly found in lymph |
Medium chain triglycerides are easier for your body to use. Here are some reasons why:
Your body absorbs them fast and sends them to your liver.
Lipases work better on medium chain triglycerides than on long-chain fatty acids.
You do not need to make complex fat emulsions to absorb them.
People with stomach problems often do better with medium chain triglycerides.
Medium chain triglycerides have a simpler way to get absorbed in your gut. If you have trouble digesting fat, these fats may be easier for you. Long-chain fatty acids need more steps and take more time to get absorbed.
Metabolism and Energy
MCTs and Quick Energy
When you eat foods with medium chain triglycerides, your body uses them fast. These fats go right to your liver after you eat them. Your liver breaks them down quickly using β-oxidation. This makes energy that your cells can use right away. Your body does not need to store these fats first. Because of this, you get a quick burst of energy after eating medium chain triglycerides.
Here is a table that shows how your body handles different types of fat:
Feature | Medium-Chain Triglycerides (MCTs) | Long-Chain Fatty Acids (LCTs) |
|---|---|---|
Absorption | Rapidly absorbed via portal vein | Slower absorption |
Metabolism | Quickly metabolized in the liver | Metabolized in various tissues |
Pathway | β-oxidation and citric acid cycle | β-oxidation in mitochondria |
End Products | Carbon dioxide, acetate, ketone bodies | Energy, carbon dioxide |
Medium chain triglycerides give you energy fast. They do not stay in your body as stored fat. This makes them good if you need quick fuel for your brain or muscles.
LCTs and Slow Metabolism
Long-chain fatty acids work in a slower way. Your body takes longer to absorb these fats. After you eat them, they move through your lymph system before reaching your blood. Your body stores a lot of this fat in fat cells for later. When you need energy, your body breaks down these fat stores. This takes more time. Long-chain fatty acids give you energy slowly over a longer time. They help your body save energy for when you do not eat.
Note: Long-chain fatty acids have more carbon atoms. This means your body can get more energy from each one. But you have to wait longer to use it.
Impact on Ketosis
Medium chain triglycerides help your body make more ketones. Ketones are special molecules your liver makes when you eat few carbs. These molecules give your brain and muscles energy. Even small amounts of medium chain triglycerides can raise your blood ketone levels. For example, taking 10–15 grams of these fats can increase plasma ketones to 0.5–1.0 mmol/L.
Here is a table that shows how medium chain triglycerides affect ketosis:
Evidence Description | Findings |
|---|---|
MCTs supplementation increases β-hydroxybutyrate concentrations | Supports nutritional ketosis during ketogenic diets |
MCTs enhance energy expenditure and reduce adiposity | Contributes to body weight loss |
kMCTs raise plasma ketones to 0.5–1.0 mmol/L | When taken as a 10–15 g dietary supplement |
If you follow a ketogenic diet, medium chain triglycerides help you reach ketosis faster. They also help your body use fat for energy instead of storing it. This can help you lose weight and give you steady energy all day.
Health Effects
Benefits of MCTs
Medium chain triglycerides can help your health in many ways. People use these fats for fast energy and to help with weight. Studies say medium chain triglycerides may help you lose more weight than long-chain fatty acids. They might also help lower blood triglyceride levels and improve insulin resistance.
Medium chain triglycerides are easier to digest. They do not need complex fat emulsions.
Some studies say these fats may help your brain and memory. But not all studies agree.
Here is a table that shows what research says about medium chain triglycerides and brain health:
Study Type | Findings | Notes |
|---|---|---|
Clinical Trials | Medium chain triglycerides may help thinking | Some studies show benefits, but some have design problems |
Meta-analyses | May help with brain health | Not all studies agree, and some show no benefit |
Laboratory Studies | May help brain health | No proof yet for long-term effects or stopping dementia |
Tip: If you have trouble digesting fat emulsions, medium chain triglycerides may be easier for you.
Benefits of LCTs
Long-chain fatty acids are important for your health. Some, like omega-3s, help your brain, eyes, and heart. These fats can lower swelling and protect your cells. You find long-chain fatty acids in fish, nuts, and some plant oils.
Here is a table that lists some health benefits of long-chain fatty acids:
Health Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
Help with brain diseases | |
Cancer and diabetes | Omega-3 fatty acids may help with cancer and diabetes. |
Eye health | DHA and EPA may help prevent eye problems and keep eyes healthy. |
Gene control | EPA and DHA may help control genes linked to obesity and other diseases. |
Help with thinking | DHA helps protect brain cells and may help you think better. |
You need fat emulsions to absorb long-chain fatty acids. These fats give you health benefits that last a long time. They help your body in more ways than just giving energy.
Potential Drawbacks
Eating too much fat from some sources can cause problems. Some studies say medium chain triglycerides can raise your total cholesterol and LDL cholesterol, like palm oil. They may also make your blood triglyceride levels go up.
Evidence Type | Findings |
|---|---|
MCT Consumption | May raise total cholesterol (TC) and LDL cholesterol (LDL-C) |
Triglycerides | May raise triglyceride (TG) levels more than other oils |
CVD Risk | We do not know yet if these fats change heart disease risk |
Long-chain fatty acids, especially saturated ones, may raise your risk of heart disease. Some research says these fats can raise cholesterol and may not be good for your heart if you eat too much. Always think about the type and amount of fat you eat to keep your heart healthy.
Practical Uses

When to Use MCTs
You may want to use medium chain triglycerides in special situations. Doctors often recommend these fats for people with certain health problems. For example, if you have very long-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase (VLCAD) deficiency, you may need MCTs. This condition makes it hard for your body to use long-chain fatty acids for energy. MCTs give you a safe source of energy and help prevent heart problems.
Condition | Recommendation |
|---|---|
VLCAD deficiency (especially with symptoms) |
Athletes and non-athletes use MCTs in different ways. Sports research shows that MCTs do not help athletes perform better. In fact, they may even harm your blood fat levels. If you are not an athlete but enjoy regular activity, small amounts of MCTs might help you exercise longer.
Group | Findings |
|---|---|
Athletes | No clear performance boost; may worsen blood fat levels |
Non-Athletes | Low doses may help you exercise longer before feeling tired |
You can also use MCTs if you have trouble digesting fat. MCTs move straight to your liver and give you quick energy. Your body does not need to break them down as much as other fats.
When to Use LCTs
Long-chain fatty acids play a big role in your daily diet. You need these fats for brain health, eye health, and to protect your heart. Foods like fish, nuts, and plant oils give you these important nutrients. If you want to support your body’s long-term health, you should include these fats in your meals. Your body stores them for future energy needs and uses them to build cell walls.
Note: If you have a medical condition that affects fat digestion, talk to your doctor before changing your intake of long-chain fatty acids.
Tips for Diet
You can balance both types of fat in your diet for the best results. MCTs give you fast energy and may help you manage your weight. They do not need chylomicrons to travel in your body, so your liver can use them right away. This process can help you burn more calories and may lower your body fat over time. Long-chain fatty acids take longer to digest and store, but they support your body in many ways.
Choose a mix of healthy fats from different foods.
Use MCT-rich foods like coconut oil if you need quick energy.
Eat fish, nuts, and plant oils for long-chain fatty acids.
Watch your total fat intake to keep your heart healthy.
Tip: Replacing some long-chain fatty acids with MCTs may help you lose weight and boost your energy. Always check with a healthcare provider before making big changes to your diet.
You now know that medium chain triglycerides and long-chain fatty acids work differently in your body. Here is a quick look at what research shows:
Key Findings | MCTs | LCFAs |
|---|---|---|
Absorption | Fast, go to liver | Slow, travel in blood |
Triglyceride Levels | Lower after meals | Higher after meals |
You should choose fats based on your health goals:
Use coconut oil for daily cooking.
Try MCT oil if you need more energy or have special health needs.
For more details, look for articles on how MCTs help with weight, satiety, and special diets.
FAQ
What are the main benefits of using MCT oil?
You get quick energy from MCT oil. Your body digests it fast. Many people use it to help with weight loss or to boost brain power. Some athletes use it for extra fuel.
Can you cook with MCT oil?
You should not use MCT oil for high-heat cooking. It has a low smoke point. You can add it to smoothies, salad dressings, or coffee for extra energy.
Are MCTs safe for everyone?
Most people can use MCTs safely. Some people may feel stomach upset or cramps if they take too much. Start with a small amount and see how your body reacts.
Do LCTs have health benefits too?
Yes! LCTs give you important fats like omega-3s. These help your heart, brain, and eyes. You find LCTs in fish, nuts, and plant oils. Your body needs both MCTs and LCTs for good health.







