When considering pea protein vs whey protein, you might wonder which is the better choice for your needs. Both are effective for building muscle. In fact, one study found that pea protein increased muscle size by 20.2%, which was even more than whey protein. For those looking for plant-based or lactose-free options, pea protein vs whey protein is a common comparison, and many choose pea protein for its dietary benefits. On the other hand, whey protein is known for its fast digestion and high leucine content. As more people seek plant-based protein for health reasons and cleaner ingredients, the debate of pea protein vs whey protein continues to grow. Today, there are plenty of options available for both.
Protein Type | Muscle Gain | Dietary Restrictions |
|---|---|---|
Whey | High because it has a lot of leucine and digests fast | Not good for people who avoid animal products |
Pea | Muscle gain is similar to whey and works for plant-based diets | Best for people with special diet needs |
Key Takeaways
Pea protein and whey protein help muscles grow. Pick one based on what you eat and like. Whey protein breaks down fast and has more leucine. This helps you recover quickly after exercise. Pea protein comes from plants and has no lactose. It is gentle on your stomach. This is good for people with special diets. Both proteins can help you lose weight. They make you feel full longer. Pea protein usually has fewer calories and less fat. Pea protein often costs less money. It is better for the environment than whey protein. This makes it a smart pick if you want to save money.
Pea Protein vs Whey Protein Nutrition

Macronutrient Breakdown
When you look at pea protein vs whey protein, you will see some differences in their nutrition. Both give you a good amount of protein in each serving. The exact numbers can change with different brands. Here is a table that shows how they compare:
Protein Source | Serving Size | Calories | Protein (g) | Carbohydrates (g) | Fat (g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Pea Protein Isolate | 30 grams | 120 | 25.2 | 0.5 | 2 |
Pea Protein Concentrate | 30 grams | 130 | 23.5 | 4 | 2.2 |
Whey Protein Concentrate | 32 grams | 130 | 25 | 3 | 2 |
Whey Protein Isolate | 32 grams | 120 | 27 | <1 | 0.5 |
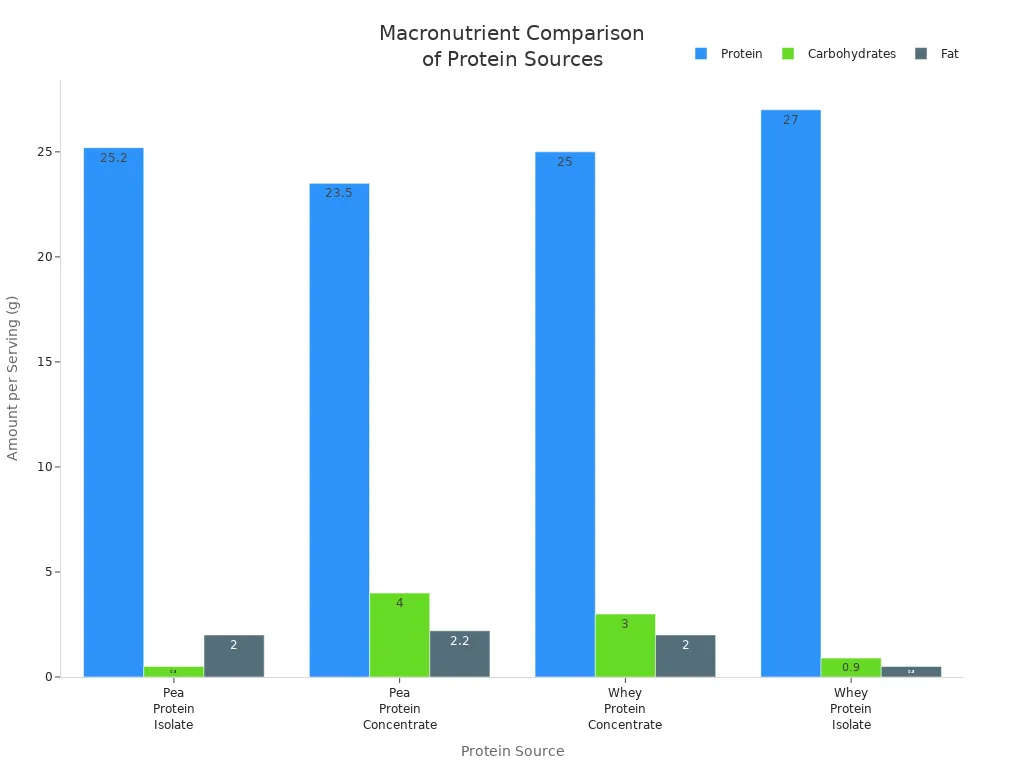
Both pea and whey protein isolates have low carbs and fat. This makes them good if you want more protein without extra calories. Whey protein isolate usually has the most protein per serving. Pea protein is close behind. If you want to eat less carbs, both isolates are good choices.
Amino Acid Profile
Amino acids help your body build muscle. Pea protein and whey protein both have many essential amino acids. There are some differences between them.
Essential Amino Acid | Whey (g per 100g protein) | Pea (g per 100g protein) |
|---|---|---|
Histidine | 1.98 | 2.71 |
Isoleucine | 6.20 | 4.69 |
Leucine | 11.52 | 8.07 |
Lysine | 9.98 | 7.45 |
Methionine + Cysteine | 4.61 | 3.15 |
Phenylalanine + Tyrosine | 6.84 | 8.23 |
Threonine | 7.94 | 3.47 |
Tryptophan | 1.53 | 0.88 |
Valine | 6.27 | 5.21 |
Total (Sum) | 57.87 | 44.86 |
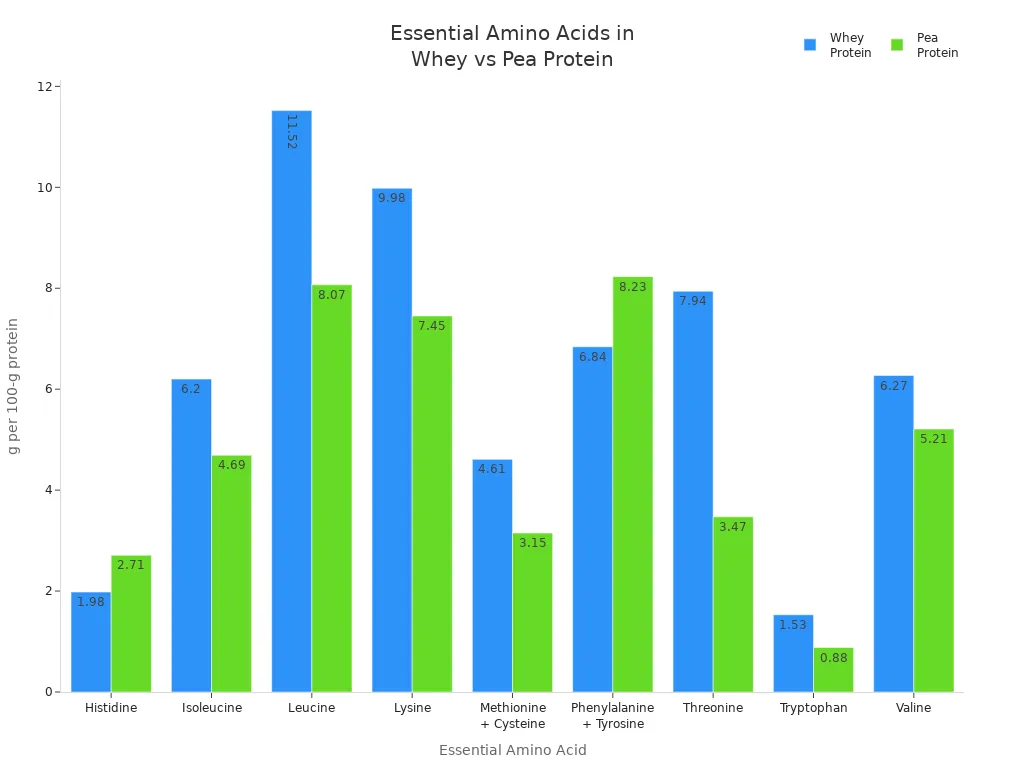
Whey protein is a complete protein. This means it has all nine essential amino acids. Pea protein is almost complete but has less methionine. Pea protein gives you more histidine and phenylalanine than whey. Leucine is important for building muscle. Whey protein has more leucine, which helps your muscles grow after exercise.
Tip: You can mix pea protein with other plant proteins like rice protein. This helps you get a complete amino acid profile.
Key Micronutrients
Protein shakes also give you vitamins and minerals. Here is how pea protein and whey protein compare for micronutrients:
Micronutrient | Pea Protein (30g) | Whey Protein (30g) |
|---|---|---|
Calcium | 87 mg (7% DV) | 130 mg (10% DV) |
Potassium | 31.5 mg (1% DV) | 166 mg (4% DV) |
Sodium | 345 mg (15% DV) | 48 mg (2% DV) |
Iron | 7.5 mg (42% DV) | 0 mg (0% DV) |
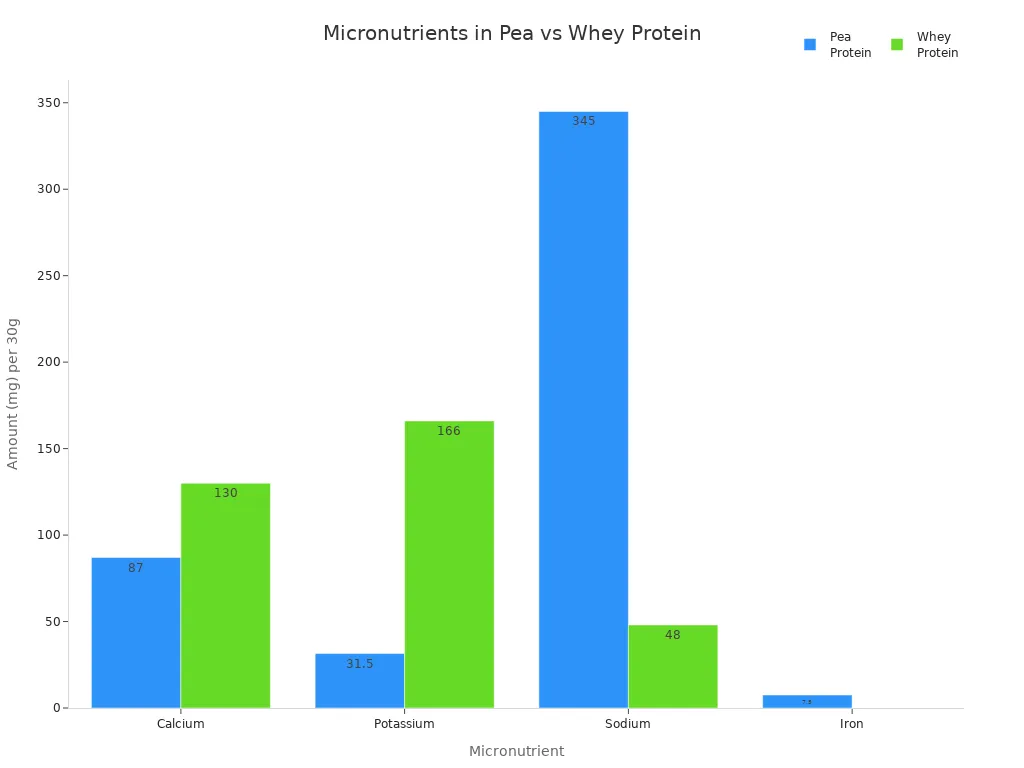
Pea protein has a lot of iron. This is good if you eat a plant-based diet.
Whey protein has more calcium and potassium. These help your muscles and bones stay strong.
Pea protein has more sodium. Remember this if you need to watch your salt.
Pea protein and whey protein both have good points. Whey protein is great because it has all the essential amino acids and more leucine. This makes it good for muscle growth and recovery. Pea protein is better if you want more iron or need a plant-based choice. Both can help you get enough protein every day, whether you play sports or just want to be healthy.
Muscle Gain Comparison
Effectiveness for Strength
If you want to get stronger, you might wonder which protein is better. Pea protein and whey protein both help you build muscle. You need to do resistance training for best results. Some studies say pea protein works as well as whey protein. One study showed people who used pea protein had bigger biceps. Whey protein helped too, but pea protein did a little better in that group.
Here’s what research found:
Study Title | Findings | Conclusion |
|---|---|---|
Pea proteins oral supplementation promotes muscle thickness gains during resistance training: a double-blind, randomized, Placebo-controlled clinical trial vs. Whey protein | People who took pea protein had bigger biceps than those who took whey or a placebo. | Pea protein is a good choice for building muscle during resistance training. |
Efficacy of Pea Protein Supplementation in Combination with a Resistance Training Program on Muscle Performance in a Sedentary Adult Population | Both pea and whey protein made biceps bigger after 12 weeks. There was no big change in muscle performance after just 5 days. | Both proteins help muscle grow over time. |
Strength is important too, not just muscle size. In one study, people who used pea protein got 16.1% stronger in 84 days. People who used whey protein got 11.1% stronger. Both groups liked their results. Both proteins were safe to use.
Pea protein and whey protein both help you get stronger.
You can pick either one for muscle gain if you work out often.
Leucine and Recovery
Leucine helps your muscles heal after you exercise. Whey protein has more leucine than pea protein. This means whey protein may help your muscles fix themselves faster and grow more.
Protein Type | Leucine Content (g/100g) | Effect on Muscle Recovery |
|---|---|---|
Whey Protein | 23.7 | Helps muscle recovery and growth more |
Pea Protein | 17.9 | Still helps, but not as much as whey |
Whey protein has about 24% more leucine than pea protein.
More leucine can help your muscles recover faster.
If you want quick recovery, whey protein might be better.
When you look at pea protein vs whey protein for muscle gain, both help you get stronger and build muscle. Whey protein may help you recover a little faster because it has more leucine. Pea protein is still a great pick, especially if you want a plant-based choice.
Weight Loss Benefits
Satiety and Appetite
When you try to lose weight, feeling full after eating can help you eat less. Both pea protein and whey protein can help you feel satisfied. Studies show that pea protein boosts satiety almost as much as whey protein. You might notice that you do not feel as hungry after a shake with either one.
Here is a quick look at how they compare:
Protein Source | Effect on Satiety | Energy Intake |
|---|---|---|
Pea Protein | Modest increase | No differences |
Whey Protein | Increased satiety | Lowered intake |
Pea protein enhances satiety similarly to whey protein.
Both can be healthy choices if you want to control your appetite.
Some research found that soups with protein helped people eat less than soups without protein. People who had pea protein felt a bit fuller, while those who had whey protein felt less hungry. If you want to manage your hunger, either option can work for you.
Calorie and Fat Content
Calories and fat matter when you want to lose weight. You want a protein that gives you what you need without extra calories. Plant-based protein powders, like pea protein, usually have fewer calories and less fat than whey protein. This can help you keep your calorie intake lower each day.
Pea protein often has lower calorie and fat content.
This makes it easier to stay in a calorie deficit, which is important for weight loss.
Plant proteins also digest more slowly, so you may feel full longer.
When you compare pea protein vs whey protein for weight loss, both can help you feel full and support your goals. If you want fewer calories and less fat, pea protein might be the better pick. Whey protein also works well, especially if you like the taste or want faster digestion.
Digestibility and Absorption
Digestive Tolerance
When you choose a protein powder, you want it to feel good in your stomach. Some people have problems with whey protein. You might get bloating, cramps, or diarrhea after drinking it. These problems happen if you cannot handle lactose or have milk allergies. Here are some common stomach issues with whey protein:
Constipation
Diarrhea
Bloating
Stomach pain
Pea protein is usually easier for your stomach. Most people feel fine after using it. If your stomach is sensitive or you do not want dairy, pea protein could be better for you.
Let’s see how well your body digests these proteins, especially as you get older:
Protein Source | |
|---|---|
Whey | 20% |
Rice | 20% |
Pea | 10% |
Wheat | 4% |
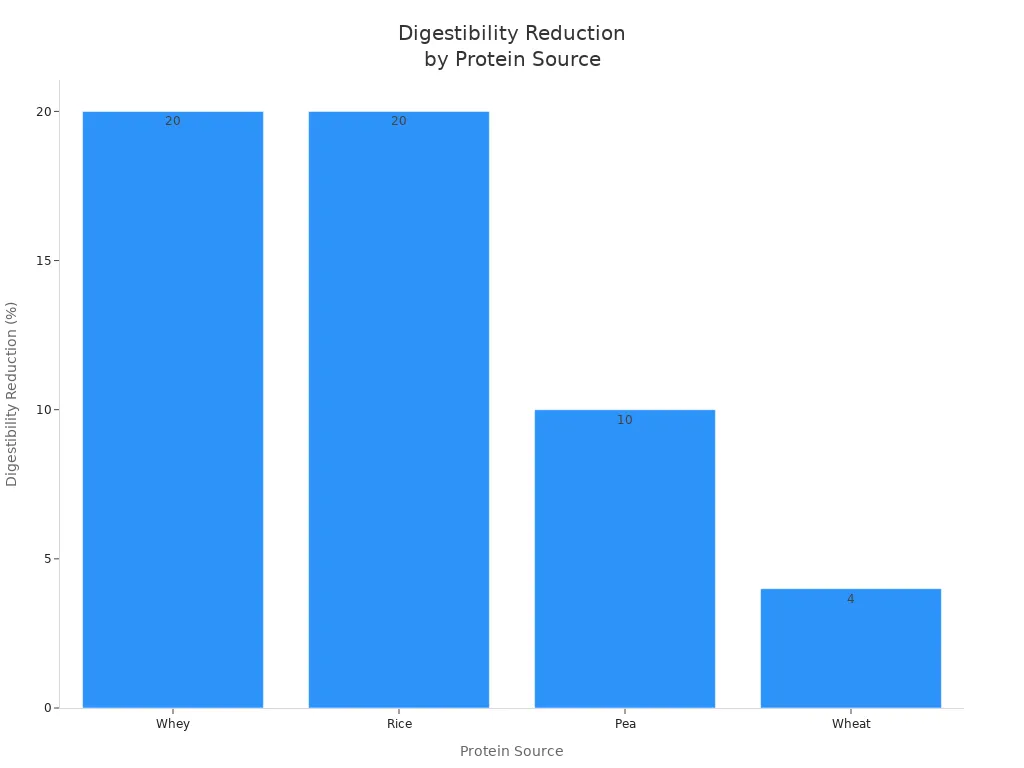
Pea protein is easier to digest than whey protein, especially for older people. If you want a protein that is gentle on your stomach, pea protein is a smart choice.
Tip: If you often feel bloated or get cramps after protein shakes, try switching to pea protein. Your stomach might thank you!
Absorption Rates
How fast your body takes in protein is important, especially after you work out. Whey protein gets into your body quickly. That is why many athletes use it right after exercise. You get amino acids fast, which helps your muscles heal.
Pea protein goes into your body more slowly. This gives you a steady supply of amino acids over time. Slow absorption can help your muscles repair and keep you full longer.
Studies show that heating does not change how fast pea protein leaves your stomach or how your body uses its amino acids. Both whey and pea protein isolates work well for appetite and energy. Their absorption rates are about the same in real life, so you can pick either one for your needs.
If you want to recover fast after a workout, whey protein is a good pick. If you want a steady release or have a sensitive stomach, pea protein might be better for you.
Allergies and Dietary Suitability
Lactose Intolerance
Do you feel sick after drinking a protein shake? You might have lactose intolerance. Many people have this problem. Here are some facts:
About 65% of people cannot digest lactose well after childhood.
Lactose intolerance makes regular whey protein hard to use because it comes from milk.
You may get stomach pain, gas, or diarrhea if you drink whey protein with lactose.
Whey protein isolate and hydrolysate have less lactose. These types are better for people with lactose intolerance.
If you want to avoid these problems, try pea protein. It does not have lactose, so your stomach will probably feel better.
Vegan and Vegetarian Options
Are you vegan or vegetarian? You need to pick the right protein for your diet. Here is a table to help you compare:
Feature | Pea Protein | Whey Protein |
|---|---|---|
Source | Plant-based (yellow split peas) | Animal-based (dairy) |
Allergen-friendly | Hypoallergenic, free from major allergens | May cause issues for lactose intolerant individuals |
Vegan suitability | Suitable for vegans | Not suitable for vegans |
Amino acid profile | Complete amino acid profile | Complete amino acid profile |
Digestibility | Easily digestible | May cause digestive issues |
Environmental impact | Sustainable choice | Less sustainable due to animal farming |
If you want a protein for vegans, pea protein is best. Whey protein comes from milk, so it does not work for vegans. When you compare pea protein vs whey protein, think about your food choices and what matters to you.
Allergy Risks
Can these proteins cause allergies? Most people do not have problems with pea protein or whey protein. But there are some things to know:
Some people with peanut allergies have reacted to pea protein. The risk is higher because pea protein powder has more protein than whole peas.
Peas are not a common allergen, so many people do not know about this risk.
Studies show pea protein can cause allergic symptoms in some cases, like higher levels of IgE and histamine.
Whey protein can cause problems for people with milk allergies.
Note: If you have a peanut allergy or other food allergies, talk to your doctor before trying a new protein powder.
Pick the right protein by thinking about your body and your diet. Always check the label and pay attention to how you feel.
Cost and Environmental Impact

Price Comparison
When you buy protein powder, price is important. You want to save money and get good value. Pea protein usually costs less than whey protein. Most brands sell pea protein for a lower price. Grass-fed whey protein can be about 50% more expensive than normal whey. You pay more for special whey, but you do not always get extra protein.
Whey protein costs more, especially if it is grass-fed or organic.
You can save money if you pick pea protein for your shakes.
If you want to spend less, pea protein is a smart pick. You get enough protein and keep more money in your pocket.
Sustainability
You may want to help the earth when you choose your protein. Pea protein is better for the planet than whey protein. Pea plants need less water to grow. Dairy cows need lots of water and food, so whey protein is not as eco-friendly. Pea plants also help the soil by adding nitrogen. This means farmers use fewer chemicals.
Pea protein uses much less water than whey protein.
Pea plants make the soil healthier and need less fertilizer.
Making pea protein creates fewer greenhouse gases than making whey protein.
Picking pea protein helps lower your carbon footprint.
Many companies use special ways to farm and make protein to protect the earth. Here is a table with some top sustainability practices:
Sustainability Practice/Certification | Description |
|---|---|
Carbon-Friendly Crop | Peas cut carbon emissions by up to 85% compared to animal proteins. |
Regenerative Agriculture | Uses non-GMO seeds and helps soil, water, and wildlife. |
Water Conservation | Grows drought-tolerant peas and uses smart irrigation. |
Zero-Waste Manufacturing | Uses every part of the pea and recycles water and waste. |
Traceability | Tracks peas from seed to final product for safety and quality. |
USSEC Sustainable Soy Assurance Protocol | Follows strict rules for sustainable soybean farming. |
If you want to help the planet, pea protein is a great choice. You support cleaner farming and less pollution with every scoop. 🌱
How to Choose: Pea Protein vs Whey Protein
For Muscle Building
If you want to build muscle, you have two strong options. Whey protein digests fast and gives your muscles a quick boost of amino acids. Pea protein works a bit differently. Your body digests it more slowly, so you get a steady supply of nutrients. Both help you gain muscle, especially if you are new to lifting weights. Here are some things to think about:
Pea protein has a high nutritional quality. Its Protein Digestibility Acid Corrected Amino Acid Score is 92.8%, which is close to whey.
Whey protein gives you a quick spike in amino acids, but pea protein keeps them coming for longer.
Studies show pea protein can help you grow bigger muscles, especially if you just started resistance training.
Tip: If you want fast recovery after workouts, whey might be your pick. If you want steady muscle support, pea protein is a great choice.
For Weight Loss
Trying to lose weight? Both proteins can help you feel full and keep your muscles strong. A study with sixty people compared pea protein, whey protein, and a carb powder over 12 weeks. The main goal was to see how much muscle people kept while losing weight. The study also looked at body weight, energy use, and heart health.
Protein Type | Helps With Satiety | Supports Muscle While Losing Weight |
|---|---|---|
Pea Protein | Yes | Yes |
Whey Protein | Yes | Yes |
You can use either one for weight loss. Both help you feel satisfied and protect your muscles.
For Dietary Needs
Your diet and allergies matter when you pick a protein. Here are some quick facts:
Pea protein is perfect if you cannot have dairy or if you are vegan.
Whey protein is not good for people with dairy allergies.
Pea protein is a top pick for those with dietary restrictions.
Protein Type | Suitable For |
|---|---|
Pea Protein | Dairy intolerance, vegan diets |
Whey Protein | Not suitable for dairy allergies |
When you look at pea protein vs whey protein, think about your goals, your stomach, and your diet. You can find the right fit for your needs!
Picking pea protein or whey protein depends on your needs. Here is a simple chart:
Nutritional Aspect | Pea Protein | Whey Protein |
|---|---|---|
Protein Content | High | High |
Amino Acids | All, low methionine | Complete, high BCAAs |
Iron | Higher | Lower |
Calcium & Potassium | Lower | Higher |
Fiber | Higher | Lower |
Absorption | Slower | Faster |
Pea protein is good if you want plant-based or allergy-friendly choices. It also costs less than whey protein. Whey protein is great for building muscle and fast recovery. Think about what you want, how much you can spend, and if you have food allergies. You get to choose what is best for your body and your life! 💪🌱
FAQ
Is pea protein or whey protein better for sensitive stomachs?
If you have a sensitive stomach, you might feel better with pea protein. It’s easier to digest and less likely to cause bloating or cramps. Whey can upset your stomach, especially if you have trouble with dairy.
Can you build muscle as fast with pea protein as with whey?
Yes, you can! Studies show pea protein helps you gain muscle just like whey. You need to work out and eat enough protein. Both options support muscle growth when you use them right.
Does pea protein taste different from whey protein?
Pea protein has a mild, earthy taste. Whey protein tastes creamier and blends easily. You might notice a difference, but you can mix both with fruits or flavors to improve the taste.
Is pea protein safe for people with allergies?
Most people can use pea protein safely. If you have a peanut allergy, check with your doctor first. Pea protein is not a common allergen, but it’s always smart to be careful.







