You may ask if whey protein sarcopenia solutions really help older people. New clinical reviews say whey protein, with resistance exercise, can help older adults gain muscle and strength:
-
Systematic reviews show big gains in muscle with whey protein and exercise.
-
Studies show better physical performance and muscle health, even with vitamin D.
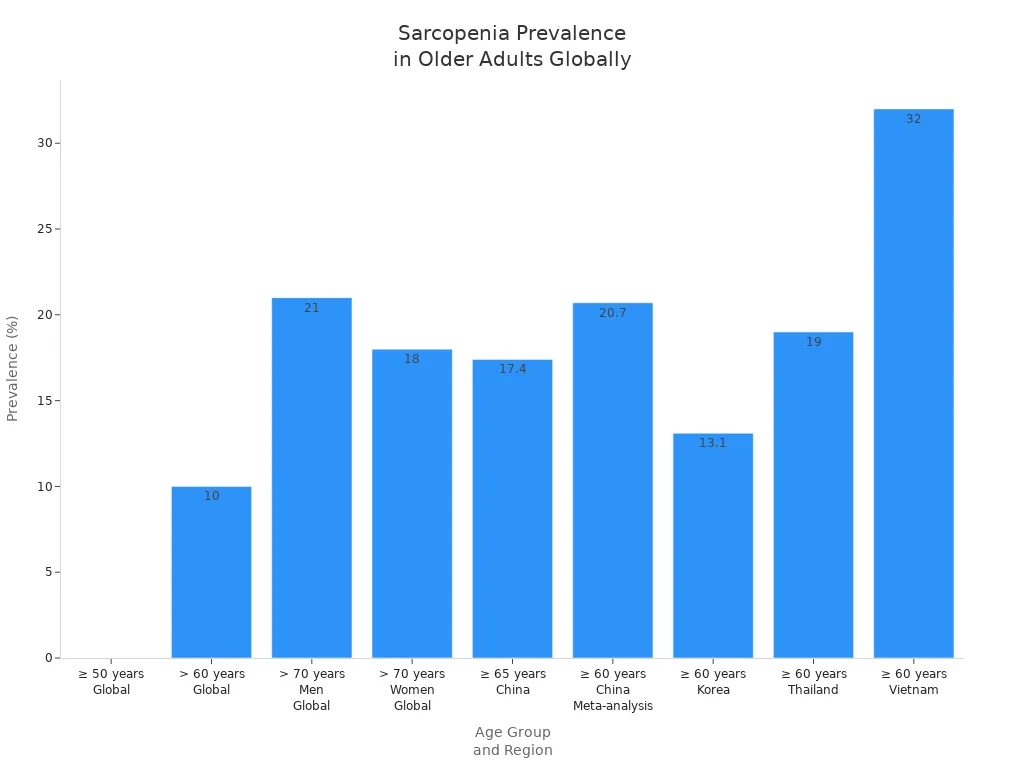
Sarcopenia affects up to 29% of adults over 50 around the world. Losing muscle makes daily tasks harder and can take away your independence. Eating well and doing strength exercises help you stay strong as you get older.
Key Takeaways
-
Whey protein and resistance exercise help older adults get stronger. They also help build more muscle.
-
Try to eat 1.2 to 1.6 grams of protein for each kilogram you weigh every day. This helps your muscles stay healthy as you get older.
-
Eat protein at different times during the day. Try to get at least 30 grams of good protein in each meal. This helps your muscles grow better.
-
You can add whey protein to your food. You can also drink it after you exercise. This helps your muscles heal and get bigger.
-
Talk to your doctor before you start any new supplement. This is very important if you already have health problems.
Whey Protein Sarcopenia Evidence
Clinical Effectiveness
You might ask how whey protein sarcopenia solutions help older people. Many studies say whey protein helps you build muscle if you also exercise. Whey protein by itself may not make you much stronger or help every part of your health. You need to do resistance training with it for the best results.
-
Whey protein sarcopenia programs work best if you pay attention to when and what kind of protein you eat.
-
How long you use whey protein and your age can change how much it helps you.
-
Experts say you should have a plan that fits you, because everyone is different.
Doctors and scientists use different ways to see if whey protein sarcopenia treatments work. Here is a table that shows the main things they check:
|
Outcome Measure |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Skeletal Muscle Mass |
Measurement of muscle mass in the body. |
|
Muscle Strength |
Assessment of the force exerted by muscles. |
|
Walking Speed |
Speed at which an individual can walk. |
|
Physical Performance |
Overall ability to perform physical tasks. |
|
Dynamic Balance |
Ability to keep balance while moving. |
Tip: Eating whey protein after you exercise can help your muscles get stronger and recover faster.
Key Studies
Scientists have checked many studies to see how whey protein sarcopenia plans help older people. Meta-analyses and systematic reviews show what works best. These studies say whey protein, with resistance training, can help you gain muscle and move better.
|
Outcome |
SMD |
95% CI |
|---|---|---|
|
Appendicular skeletal muscle mass index |
0.47 |
0.23, 0.71 |
|
Appendicular skeletal muscle mass |
0.28 |
0.11, 0.45 |
|
Gait speed |
1.13 |
0.82, 1.44 |
|
Handgrip strength (WP with RT vs. PLA/RC) |
0.67 |
0.29, 1.04 |
These numbers show whey protein sarcopenia programs help you walk faster and grip things better. The biggest improvements happen when you add resistance training to your plan.
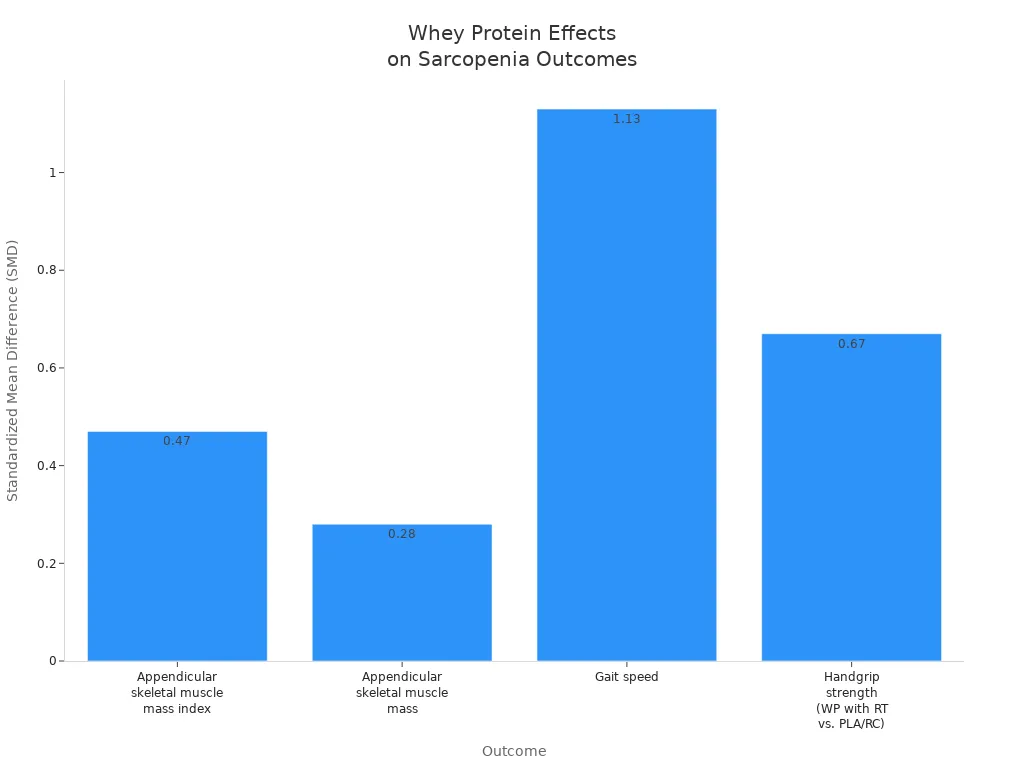
Note: The chart above shows how much muscle, walking speed, and grip strength can get better when you use whey protein with exercise.
Sarcopenia in Older Adults

Definition
Sarcopenia is a muscle disease that affects many older adults. You may notice it as a loss of strength, muscle size, and the ability to move easily. Doctors use clear steps to find out if someone has sarcopenia:
-
You start with a simple check, like the SARC-F questionnaire, to see if you might be at risk.
-
Next, you measure grip strength or how fast you can stand up from a chair.
-
If these tests show weakness, a doctor may use a DXA scan to look at your muscle quantity and quality.
-
To see how severe it is, you check how fast you walk or how well you can balance.
These steps help you and your doctor understand your muscle health and what you can do next.
Impact
Sarcopenia becomes more common as you get older. The risk grows after age 60. The table below shows how muscle strength changes with age:
|
Age Group |
Weak Strength (%) |
Intermediate Strength (%) |
Normal Strength (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
|
60 and over |
5 |
13 |
82 |
|
60–79 |
2 |
8 |
90 |
|
80 and over |
19 |
34 |
47 |
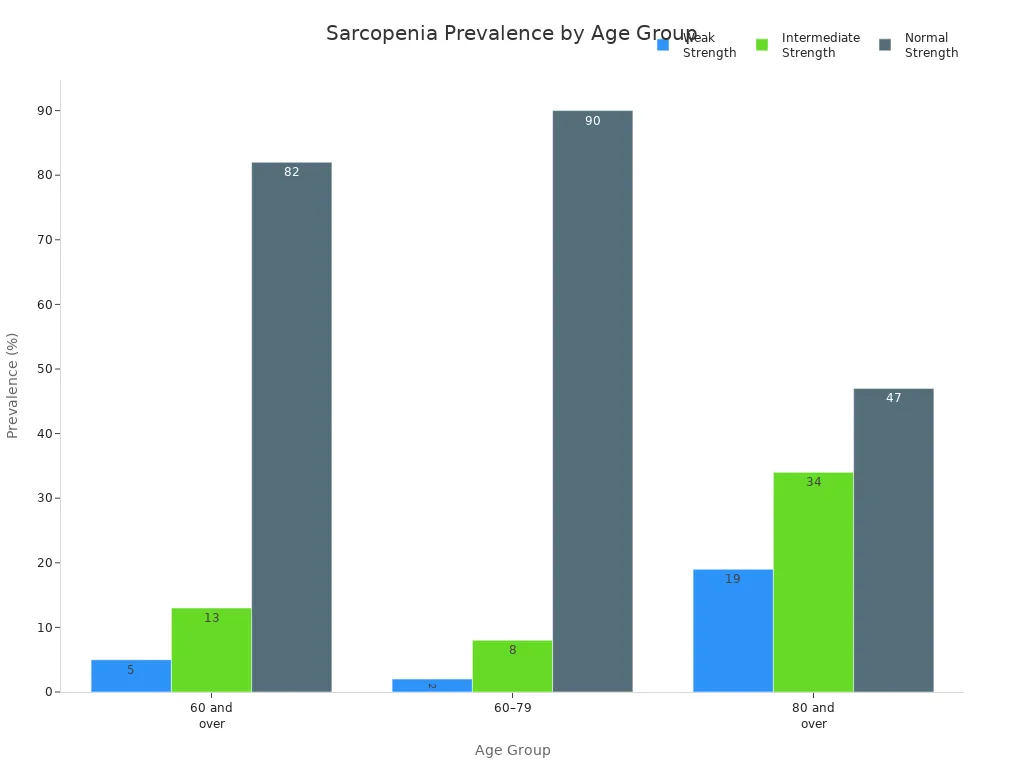
Sarcopenia can affect your daily life in many ways. You may find it harder to walk, climb stairs, or carry groceries. The disease also brings higher health costs. In the United States, hospital stays for people with sarcopenia cost about $40.4 billion each year. If you have sarcopenia, you are almost twice as likely to need hospital care. Older adults pay more for these hospital visits than younger people.
Sarcopenia also raises the risk of early death. The table below shows that people with sarcopenia have a higher mortality rate and shorter survival time than those without the disease.
|
Group |
Mortality Rate |
Mean Survival Time (days) |
95% CI |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Sarcopenic Patients |
12.87 |
10.63–15.10 |
|
|
Non-Sarcopenic Patients |
11.0% |
37.82 |
30.76–44.88 |
You can lower your risk by staying active and eating well. Many experts recommend whey protein sarcopenia programs as part of a healthy lifestyle for older adults.
Whey Protein Supplementation

Muscle Mass and Strength
You may wonder if taking whey protein helps you build muscle and get stronger as you age. Research shows mixed results, especially if you do not exercise much. Some studies say protein supplements, like whey protein, can help your muscles. Others do not find big changes. Here are some key points:
-
Whey protein may help some older adults gain muscle, but not everyone sees the same results.
-
If you do not move much, protein alone may not make you stronger.
-
One recent study found that protein by itself does not do much for muscle health. You might need other nutrients or exercise for the best results.
If you want to get the most from whey protein sarcopenia programs, you should combine protein with regular resistance training. This means lifting weights or doing exercises that make your muscles work harder.
Tip: Try to stay active and eat enough protein every day. This helps your muscles stay healthy as you age.
Physical Performance
Whey protein can also affect how well you move and balance. Studies show that when you use whey protein with resistance exercise, you may walk faster and keep your balance better. Whey protein alone does not always give you these benefits. Adding other nutrients may help even more.
The table below shows how whey protein can improve your walking speed:
|
Outcome |
Effect Size (m/s) |
Confidence Interval |
p-value |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Gait Speed |
(0.090 to 0.130) |
0.003 |
You can see that people who use whey protein with exercise walk a little faster. Even small changes in walking speed can make daily life easier and safer.
Whey Protein vs Other Proteins
Plant-Based Proteins
You may wonder how whey protein and plant proteins compare for muscle health. Whey protein is special because it has all the amino acids your muscles need. Plant proteins, like soy or pea, have different amino acids. Some plant proteins do not have much leucine. Leucine helps your muscles grow.
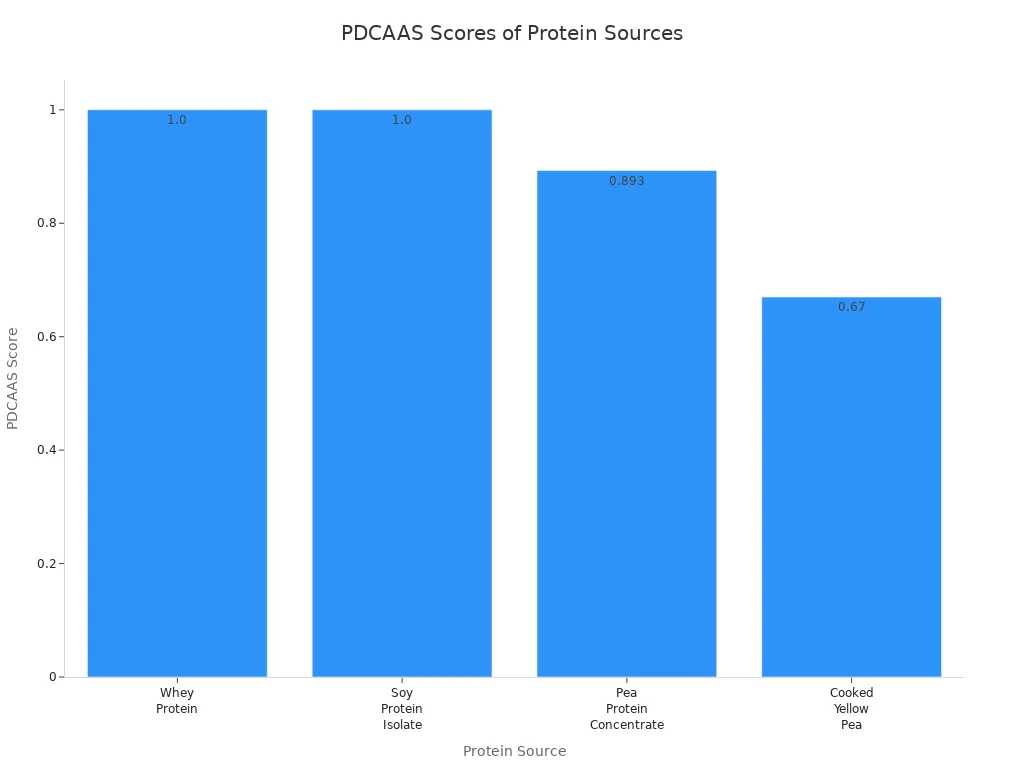
Look at this table. It shows how good each protein is:
|
Protein Source |
PDCAAS |
DIAAS |
|---|---|---|
|
Whey Protein |
1.00 |
100 |
|
Soy Protein Isolate |
1.00 |
107 |
|
Pea Protein Concentrate |
0.893 |
62 |
|
Cooked Yellow Pea |
0.67 |
N/A |
PDCAAS and DIAAS show how well your body uses protein. Whey and soy have the highest scores. Pea and cooked yellow pea have lower scores. If you pick plant proteins, you might need to eat more. You can also mix different plant proteins to get enough amino acids.
Tip: If you eat only plant foods, try mixing soy, pea, and other proteins. This helps you get more amino acids for your muscles.
Animal Proteins
Animal proteins like whey, casein, and egg have all the amino acids you need. Your body can use these proteins easily. They help your muscles grow well. Whey protein works quickly. Casein takes longer to digest. Egg protein also helps build muscle. Some studies say egg and whey work differently.
Here is what scientists found:
|
Evidence Type |
Findings |
|---|---|
|
Dairy Protein Impact |
Dairy proteins like whey and casein help muscle mass, strength, and performance. |
|
Variability in Studies |
Health and protein type change results. Comparing whey and egg is not simple. |
|
Anabolic Response |
Protein supplements work best in healthy people. The kind of protein changes results. |
You get the most from protein supplements if you stay active and eat enough protein. Whey protein often helps muscle growth more, especially with exercise.
Note: Animal proteins have more leucine and other important amino acids than plant proteins. This makes them a good choice to help stop muscle loss as you get older.
Whey Protein Intake
Recommended Amounts
You need enough protein each day to keep your muscles strong as you age. Experts suggest that older adults should aim for more protein than the standard RDA. Most studies recommend between 1.2 and 1.6 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight daily. For example, if you weigh 70 kg (about 154 pounds), you should try to get 84 to 112 grams of protein each day. Whey protein can help you reach this goal, especially if you have trouble eating enough from food alone.
Tip: Try to include high-quality protein at every meal. Whey protein shakes or powders make it easier to meet your daily needs.
Timing and Distribution
How you spread your protein during the day matters. Your muscles respond best when you eat enough protein at each meal, not just at dinner. Research shows that at least 30 grams of high-quality protein per meal helps your muscles grow and repair. Each meal should also have about 3 grams of leucine, an amino acid that triggers muscle building.
Here is a table to help you plan your protein intake:
|
Key Finding |
Details |
|---|---|
|
Optimal Protein Intake |
1.2–1.6 g/kg body weight per day |
|
Meal Distribution |
At least 30 g high-quality protein per meal |
|
Leucine Threshold |
About 3.0 g leucine per meal (from 30–35 g high-quality protein) |
|
Anabolic Response Timing |
Breakfast should include at least 30 g protein for best muscle support |
|
Protein Distribution |
Even protein at each meal works better than loading up at one meal |
Note: Meals with less than 20 grams of protein may not help your muscles as much.
With Exercise
You get the most benefit from whey protein when you combine it with resistance exercise. Lifting weights or doing strength exercises tells your muscles to grow. A clinical study found that older men who did resistance training and took whey protein gained more muscle and walked faster than those who only exercised or only took protein. The best results came from doing both together.
-
Try to do resistance exercises two or three times a week.
-
Drink a whey protein shake soon after your workout to help your muscles recover and grow.
-
Stay consistent with both your exercise and protein intake for lasting results.
🏋️♂️ Remember: Whey protein works best when you stay active and make it part of your daily routine.
Benefits and Risks
Muscle Health
Whey protein gives your muscles the building blocks they need. As you age, your body finds it harder to keep muscle. You can slow this loss by eating enough protein. Whey protein stands out because it has all the amino acids your muscles need. It also has a lot of leucine, which helps your muscles grow.
You may notice these benefits when you add whey protein to your diet:
-
Better muscle strength: You can lift more and move easier.
-
More muscle mass: Your muscles look and feel firmer.
-
Faster recovery: After exercise, your muscles heal quicker.
-
Improved balance and walking speed: You may feel steadier and walk with more confidence.
Tip: Try to eat protein at every meal. This helps your muscles stay strong all day.
Here is a quick look at how whey protein supports muscle health:
|
Benefit |
How It Helps You |
|---|---|
|
Muscle Growth |
Builds and repairs muscle tissue |
|
Strength Gains |
Increases power for daily tasks |
|
Recovery Support |
Reduces soreness after exercise |
|
Mobility Improvement |
Helps you move and balance better |
Safety
Whey protein is safe for most older adults. You should still use it with care. Some people may have mild side effects, such as stomach upset or bloating. If you have kidney disease or lactose intolerance, talk to your doctor before using whey protein.
You can follow these tips to stay safe:
-
Start with a small amount to see how your body reacts.
-
Drink plenty of water when you use protein powders.
-
Choose products with simple ingredients and no added sugar.
Note: Always check with your healthcare provider before starting any new supplement, especially if you take medicine or have health problems.
Whey protein can help you stay strong, but you must use it wisely. Listen to your body and make changes if you feel unwell.
Practical Tips
Choosing Supplements
You should pick a whey protein that helps your muscles and fits you. Look for products with lots of leucine and important amino acids. These nutrients help slow muscle loss and keep you strong as you get older.
Whey protein has leucine and other amino acids that help stop and even reverse sarcopenia. Doing resistance training and using whey protein is a strong way to keep and build muscle as you age. One big study looked at adults over 60 with sarcopenia. It showed they gained muscle and had stronger handgrip. Older men used whey protein more than casein, so whey protein is a better choice for older people.
When you buy supplements, check the label for these things:
-
At least 20 grams of protein in each serving
-
Low sugar and few extra ingredients
-
Easy-to-read ingredient list
-
Extra vitamins or minerals like calcium or vitamin D
Whey protein helps you keep muscle, recover after exercise, and keep bones healthy. It also has special parts that help your immune system.
If you have food limits or health problems, choose carefully. Some powders have lactose, which can upset your stomach. If you have kidney problems, talk to your doctor before eating more protein.
|
Consideration |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Increased Protein Needs |
Older people need more protein, especially if they are weak or sick. |
|
Renal Function |
If you have kidney disease, eat only 0.3–0.8 gm/kg/day of protein. |
|
Gastrointestinal Issues |
Some people feel dizzy after eating; start with small amounts. |
Daily Use
You can add whey protein to your food in easy ways. Mix it into oatmeal, smoothies, or yogurt. Drink a shake after you exercise to help your muscles heal.
|
Strategy |
Recommendation |
|---|---|
|
Optimal Dose per Meal |
|
|
Higher Bolus for MPS |
Up to 40 g with or without exercise |
|
Protein Distribution |
Every 3–4 hours with moderate intake |
Try to eat 25 to 30 grams of good protein at each meal. Space your meals every three to four hours. This helps your muscles grow and fix themselves all day.
-
Use whey protein to meet your daily protein goal.
-
Spread your protein between breakfast, lunch, and dinner.
-
If you cannot eat solid food, a shake is a good choice.
Tip: Always talk to your doctor before starting a new supplement, especially if you have health problems or take medicine.
You can keep your muscles strong as you get older by eating well and staying active. Whey protein with resistance training helps you get stronger and move better each day.
-
Try to eat 25 to 30 grams of protein at every meal.
-
Older people should aim for about 1.3 grams of protein for each kilogram they weigh every day.
-
Adding just 30 grams of protein daily can help you build more muscle.
Experts say it is smart to start eating healthy and moving often while you are still young. This helps you stay able to do things on your own and lowers your chance of getting hurt or sick. Always ask your doctor before you use any new supplement. Make sure you care for your muscles as you age.
FAQ
Can you take whey protein if you have diabetes?
You can use whey protein if you have diabetes. Choose products with low sugar. Whey protein may help control blood sugar after meals. Always check with your doctor before starting any new supplement.
How do you know if you need more protein?
You may feel weak, lose muscle, or heal slowly after injuries. Older adults often need more protein. Ask your doctor to check your diet and muscle health.
Tip: Try to eat protein at every meal to support your muscles.
Is it safe to use whey protein every day?
You can use whey protein daily if you do not have kidney problems or allergies. Start with small amounts. Drink plenty of water. Talk to your doctor if you have health concerns.
|
Safety Tips |
Details |
|---|---|
|
Start small |
Use one scoop first |
|
Stay hydrated |
Drink water often |
|
Check ingredients |
Avoid added sugars |
Can you use plant protein instead of whey?
You can use plant protein, like soy or pea, if you do not eat dairy. Mix different plant proteins to get all the amino acids your muscles need. Plant proteins may need larger servings.
When is the best time to take whey protein?
You get the most benefit when you take whey protein after exercise. Your muscles use protein to grow and repair. You can also add whey protein to breakfast or lunch.
🕒 Best time: Right after your workout or with a meal.

